

Is Nerve Damage From a Burn Injury Permanent?Ī burn that impacts the nerves can damage them temporarily or permanently. The exact characteristics of nerve damage from a burn injury will depend on the specific patient and the severity of the burns. These conditions can be deadly for patients depending on the case. These conditions can cause pain, weakness, or tingling and prickling (paresthesia) in the affected area. Some patients have no feeling left in the infected nerves at all due to total nerve destruction.Īt the most serious level, nerve damage from a burn injury can cause conditions such as peripheral neuropathy and nerve compression. Severe nerve damage can also cause neuropathic pains, where damaged nerve endings send incorrect and random signals to other pain centers in the body that are not close to the burn. They may persist for the duration of the patient’s recovery. These pains can be severe and feel electric. Patients also report shooting pains around burn injuries due to damaged nerves in the area. Nerve damage from burn injuries can cause sensations such as numbness, weakness, pain, tingling, burning and sensitivity to touch in patients. Symptoms of Nerve Damage From a Burn Injury A third-degree burn will also impact the nerves within the dermis.
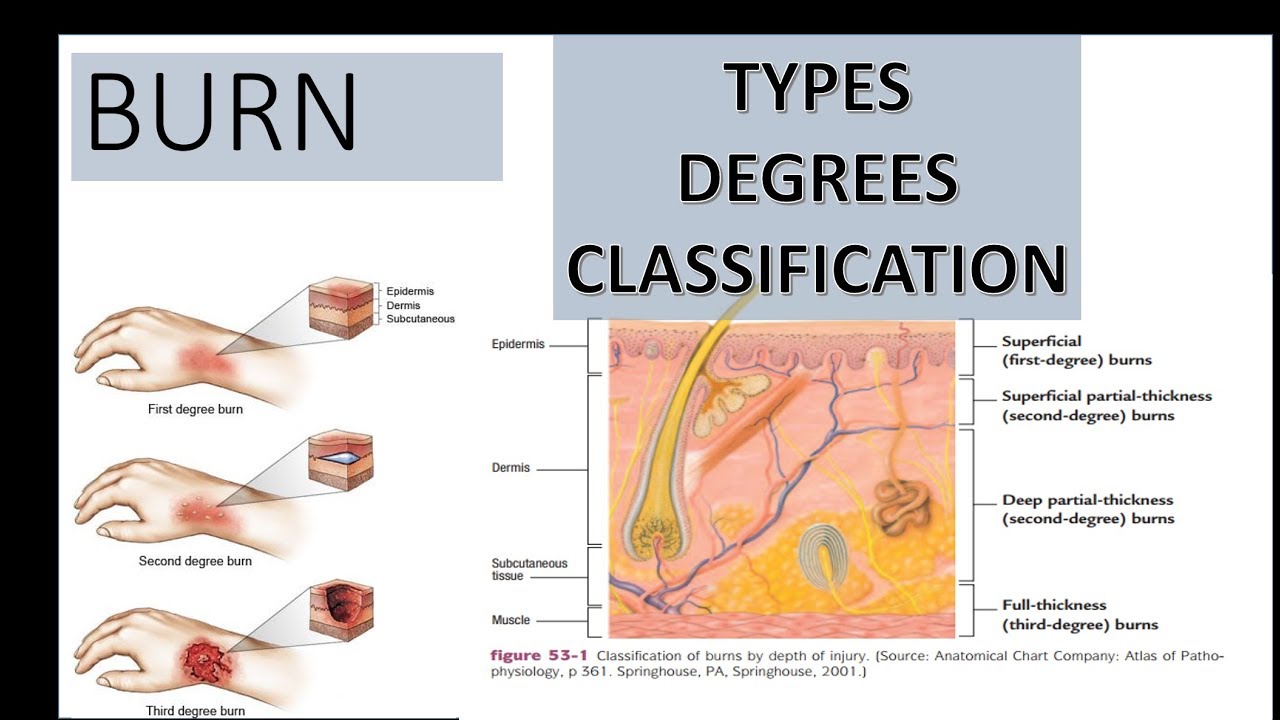
It damages the epidermis and the dermis, with the possibility of impacting the nerves. A second-degree burn, however, affects the deeper layer of tissues. A first-degree burn, the most minor type, will not reach down into the dermis. The dermis contains nerve endings that are responsible for pain sensations.
2nd or 3rd degree burn skin#
The body’s nerves are located in the thicker second layer of tissues, under the first layer of skin (the epidermis). Whether or not a burn injury impacts the nerves depends on the thickness of the burn. If a burn injury damages the nerves, this can have a significant impact on the patient’s daily life. The information your nerves process allows you to feel pain, cold, heat and touch. Other types of nerves control movements, actions and sensations. Nerves are responsible for controlling many involuntary bodily functions, including temperature regulation, blood pressure and digestion. Nerves are bundles of fibers that transmit electrical impulses to and from the brain. Whether or not a patient will experience nerve damage from a burn injury depends on the case. One of the greatest concerns with a burn injury is the potential for nerve damage. Depending on the severity of the burn, it can also impact parts of the body beneath the dermis, including the muscles and bones. A burn injury impacts the soft tissues and deeper layers of the skin. There is no sensation in the area since the nerve endings are destroyed.īurns affecting 10 percent of a child's body and those affecting 15 to 20 percent of an adult's body are considered to be major injuries and require hospitalization and extensive rehabilitation.How Common Is Nerve Damage From a Burn Injury?īurn injuries can occur in many different types of accidents, including motor vehicle collisions and workplace accidents. Third-degree burns may also damage the underlying bones, muscles, and tendons. Third-degree burns destroy the epidermis and dermis. The burn site appears red, blistered, and may be swollen and painful. Second-degree burns involve the epidermis and part of the dermis layer of skin. Second-degree -(partial thickness) burns.Long-term tissue damage is rare and usually consists of an increase or decrease in the skin color. The burn site is red, painful, dry, and with no blisters. Burns are classified as first-, second-, or third-degree, depending on how deep and severe they penetrate the skin's surface.įirst-degree burns affect only the epidermis, or outer layer of skin.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
